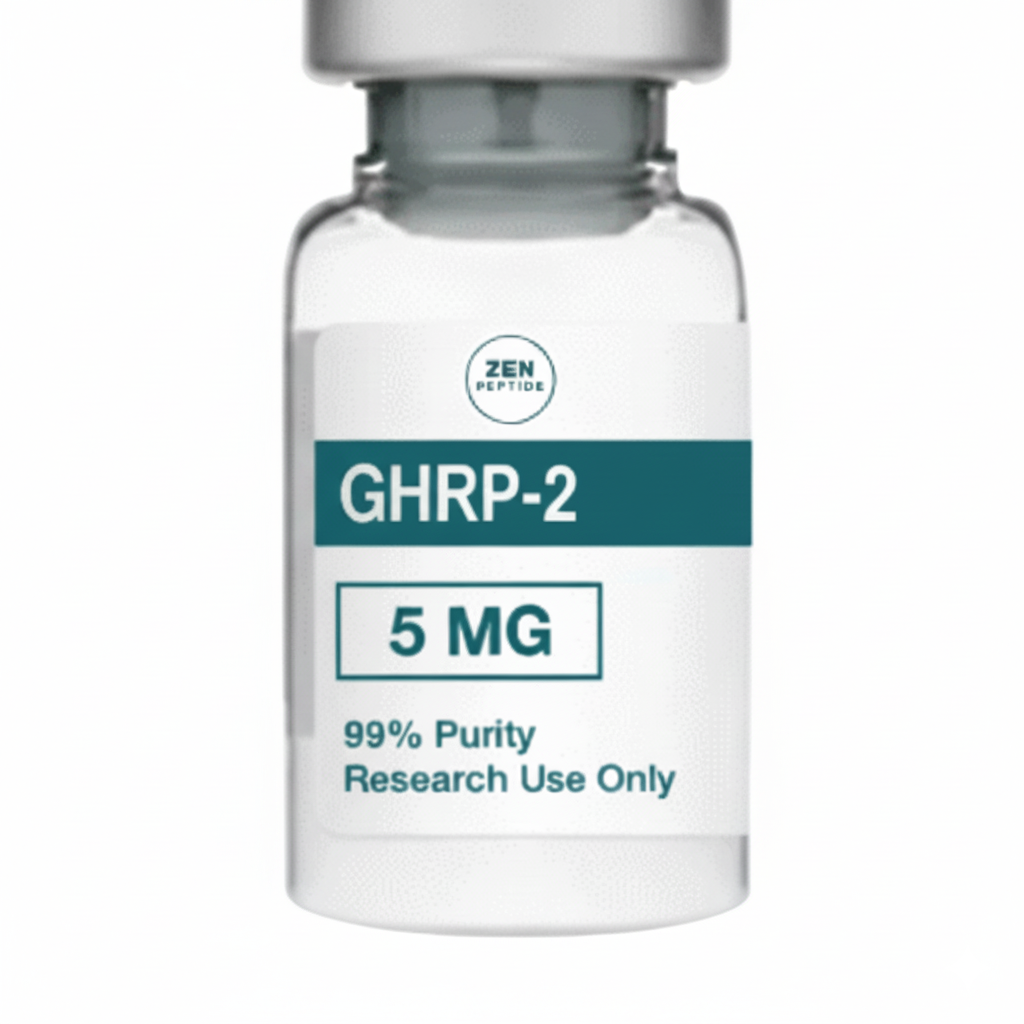
GHRP-2 ACETATE
$33.00 – $63.00Price range: $33.00 through $63.00
GHRP-2 Acetate: The Powerhouse of GH Stimulation
GHRP-2 (Growth Hormone Releasing Peptide-2) is a potent secretagogue designed to trigger a large and immediate release of growth hormone from the pituitary gland. As a synthetic ghrelin mimetic, it delivers a powerful one-two punch for GH stimulation.
While known for its impressive effectiveness in building lean muscle and accelerating fat loss, GHRP-2 is also famous for its notable effect on appetite. The “Acetate” signifies the stabilizing salt used to ensure the peptide’s purity and integrity.
Understanding GHRP-2 Acetate: A Potent Ghrelin Mimetic
GHRP-2 is a second-generation Growth Hormone Releasing Peptide (GHRP). It’s a synthetic hexapeptide that powerfully stimulates the body to release its own endogenous growth hormone. Its primary mechanism is acting as an agonist for the ghrelin/growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHSR).
How Does GHRP-2 Work? The Dual-Action Mechanism
GHRP-2’s potency comes from its ability to stimulate GH release through two distinct pathways:
- Direct Pituitary Stimulation: It binds to GHSRs on pituitary cells, directly signaling them to release their stored growth hormone.
- Hypothalamus Action: It also acts on the hypothalamus to suppress somatostatin, a hormone that acts as a “brake” on GH release. By releasing this brake, it allows for a larger and more sustained GH pulse.
This dual action makes it significantly more effective at raising GH levels than GHRH alone. A notable effect of its ghrelin mimetic action is a potential increase in hunger shortly after administration.
Key Benefits of GHRP-2 Peptide Therapy
The strong pulse of GH initiated by GHRP-2 can lead to a wide range of benefits:
- Increased Lean Muscle Mass: GH stimulates IGF-1, which promotes muscle cell growth (hypertrophy and hyperplasia).
- Accelerated Fat Loss (Lipolysis): Growth hormone helps break down fat cells for energy.
- Improved Recovery and Repair: Reduces recovery time from workouts and injuries.
- Enhanced Sleep Quality: Promotes deeper, more restorative stages of sleep.
- Anti-Aging Properties: Supports skin elasticity, bone density, and immune function.
Important Considerations: Cortisol, Prolactin, and Hunger
While very effective, GHRP-2 is less selective than newer peptides like Ipamorelin. This means it can also cause a slight increase in other hormones:
- Cortisol: The primary stress hormone.
- Prolactin: A hormone involved in lactation and immune regulation.
- Appetite: The ghrelin mimetic effect often leads to a noticeable increase in hunger.
4. FAQ
This section targets long-tail keywords and common user questions.
Frequently Asked Questions about GHRP-2
Q: How is GHRP-2 Acetate administered?
A: GHRP-2 is administered via subcutaneous (SubQ) injection, typically into the fatty tissue of the abdomen.
Q: What are the main side effects of GHRP-2?
A: The most common side effect is a significant increase in hunger shortly after injection. It can also cause a temporary, slight elevation in cortisol and prolactin levels. Some users may experience mild water retention or tingling in the hands/feet.
Q: How is GHRP-2 different from Ipamorelin or GHRP-6?
A: This is a key comparison:
- GHRP-6: The first generation. Causes a strong GH pulse and very strong hunger.
- GHRP-2: The second generation. Causes a stronger GH pulse than GHRP-6, with a slightly less intense (but still significant) hunger effect. Can slightly raise cortisol/prolactin.
- Ipamorelin: The newest generation. Causes a strong, clean GH pulse with virtually no effect on hunger, cortisol, or prolactin, making it the most selective.
Q: Can GHRP-2 be stacked with other peptides?
A: Absolutely. GHRP-2 is most effective when “stacked” with a GHRH like CJC-1295 without DAC (Mod GRF 1-29). This combination creates a powerful synergistic effect, leading to a much larger GH release than either peptide could achieve on its own.
| Dosage | 5 mg x 10vials, 10 mg x 10vials |
|---|
Be the first to review “GHRP-2 ACETATE” Cancel reply
Related products
BUY PEPTIDE
BUY PEPTIDE
BUY PEPTIDE
BUY PEPTIDE
BUY PEPTIDE
BUY PEPTIDE
BUY PEPTIDE














Reviews
There are no reviews yet.